Table of Contents
Choosing the right systems and appliances for your home can impact overall maintenance, repair, and upkeep costs. This is especially true when it comes to heating systems like furnaces.
In this article, we’ll take a look at the different types of furnaces, as well as the pros and cons that come with them.
Types of Furnaces
A furnace is a heating and cooling appliance used to heat the air and cool the water in a building. It consists of two parts: the furnace itself, which heats up the air, and the blower fan, which circulates that heated air throughout the building.
Electric Furnace
An electric furnace is a device that provides warmth for the house by heating it. An electric furnace is just like any other heater but larger and offers more warmth. While a gas furnace uses gas to produce heat from its exhaust, an electric furnace gets its power from the electricity it uses.
The exhaust from an electric furnace is heated air that can be used in different ways depending on the house’s system for using warm air (such as radiators). The heated air travels through ducts in a central heating system and then into rooms with ducts connected to them.
The hot air goes up through vents near the floor or ceiling before being blown back down again. It flows back and forth like a radiator, warming the room.
The hot airflow can also be used to warm up other rooms on the same floor with a duct system and any floors above and below. The heat from an electric furnace exhaust can be removed from the exhaust using a transfer grille.
This kind of grille distributes heat in the various rooms throughout the structure of a house or building that is large enough to have rooms with ducts in them. The transfer grille has multiple outlets for multiple rooms but only one inlet for returning warm air into the furnace’s chamber.
Natural Gas Furnace
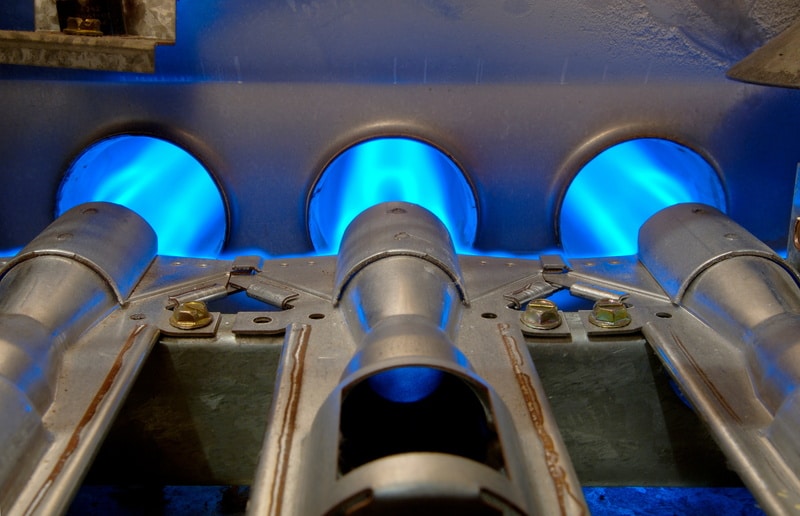
A natural gas furnace is a device that heats the interior of a home using natural gas. It is one of the most popular forced-air heating systems available for residential use.
Natural gas furnaces are highly flexible and easy to control, making them more responsive than other system types that rely on electricity or fuel oil as their heat source. They also produce less pollution than other heat sources due to their lack of carbon monoxide emissions.
The process begins with a flame that burns at over 2,000 degrees Fahrenheit while mixed with just enough atmospheric oxygen to keep it burning cleanly in an enclosed combustion chamber. This process is called combustion.
A natural gas furnace holds a supply of clean air that the burning flame has heated. This hot air is then directed through an array of louvers and funnels so that it passes into the heating ducts, eventually reaching the rooms inside of your home. These openings are often configurable and can be altered to accommodate different rooms and heating needs.
Once inside the home, your home’s hot air will circulate through ductwork thanks to natural gas furnaces’ ability to provide a constant, balanced flow of hot air throughout your home at a speedy rate of 12-22 miles per hour (25 to 45 kilometers per hour).
Furnace Pros & Cons
Furnaces are very widely used, but they aren’t for everyone. Let’s take a look at some of the pros and cons of having a furnace in your home!
Pros of Furnaces
1) No Need for Ventilation
Furnaces don’t create dangerous gases, so there is no need for exhaust fans, vents, or chimneys. This keeps harmful pollutants from escaping into the atmosphere and causing health issues in humans and animals alike.
2) Reduced Energy Consumption
Furnaces are more efficient than other heating sources. With less need for electricity and fuel, your overall energy consumption will be lower. Furnace efficiency depends on fuel type, furnace size, type of fuel used in the system, and heating requirements of your home.
3) Accessories Available
In addition to boilers, furnaces usually come with accessories such as thermostats, thermostat controls, and programmable controls. With thermostat controls, you can decide what temperature should be set at any time – ideal for those who want to sleep more comfortably at night.
4) Heating Efficiency
Furnaces are more efficient than other heating options because they use less energy and burn clean air, unlike oil or electric stoves. Furnaces use about 15% less energy for heating than gas ranges, oil stoves, and electric space heaters.
5) Low Maintenance
These furnaces are easy to maintain because you don’t have to worry about oil or electric cords getting tangled up. With no moving parts, it’s also easy to clean. Furnace cleaners often use non-toxic fuels – alcohol or propane.
As a result, your unit can be restored to its original condition with just a good vacuuming and wipedown job.
6) Fire-Safe
Most furnaces are designed to shut down automatically if they accidentally catch fire, but the risk of that happening is minimal.
7) Compliant with Existing Energy Sources in the Home
Since you likely already use electricity to power your home, the costs of converting it to heat to power a furnace are minimal.
Cons of Furnaces (Gas & Electric)
1) Gas Furnaces Don’t Last as Long As Electric
Gas furnaces require replacement after 10-15 years, whereas electric furnaces require replacing after 20-30 years.
2) Furnaces are Expensive to Maintain
Filters need to be replaced every six months and having someone come out to service a problem with your furnace can also be costly.
3) Natural Gas Furnaces are a Higher Cost Upfront
Installation for natural gas furnaces tends to cost more, especially if a supply line needs to be connected. The cost is well worth it, though. Never attempt a furnace installation on your own- call a professional HVAC service like ESCO to help. If cost is an issue, it won’t hurt to check out ESCO’s New Heating Financing option!
Alternative Home Heating System Options
Furnaces are very effective when it comes to heating most homes. But depending on the style of your home and the climate in which you live, it might be worth it to explore alternative home heating options.
Here are a few options to choose from!
Heat Pumps
A heat pump is a machine that transfers heat from one place to another, such as from the air outside your house to the inside. A heat pump can either be an air-source or ground-source system.
Air-source heat pump systems require the combustion of fuel such as natural gas or propane to produce the high temperature required for heat.
However, ground-source heat pump systems do not require fuel or combustion because they use the exothermic chemical process of a reaction between hydrogen and oxygen to produce the high temperature required for heating.
A heat pump is an excellent solution to many heating problems, especially in areas where the temperature fluctuates between seasons or outside temperatures are extremely low.
Radiant Heaters
Radiant heaters are devices that use natural or electric radiation to produce warmth. They do not actually generate heat but instead rely on the process of infrared radiation to provide warmth.
This means that they are an excellent source of heat for rooms that have a great deal of glass or reflective surfaces, as well as cold hard floors. Radiant heaters are used for a wide array of purposes.
They are perfect for warming up cold floors in bathrooms and kitchens or adding heat to areas where there is insufficient radiative heat generated by natural convection.
Space Heaters
An electric space heater is an appliance used to keep rooms warm and comfortable. Electric space heaters are typical in most homes, though they may sometimes be installed in other spaces such as offices or public areas.
They provide both heating and cooling functionality, making them convenient for the colder months of the year when a nice-sized room feels cozy without the necessity to use a whole-house central heating system.
An electric space heater operates by heating air, which gets warmed to a comfortable room temperature. They work in much the same way as a microwave; they convert electrical energy into heat that pushes heat through the air.
The power used to run an electric space heater is typically supplied by a thermostat-controlled switch and cord, so it can be deactivated when not needed, such as during summer months or when the weather is cold.
Space heaters are great to have on hand in the event of an emergency if your main heating system goes out and you’re waiting for your emergency heating service to arrive and fix the problem.
HVAC Systems
An HVAC (Heating, Ventilating, and Air Conditioning) System is an engineered system of circulating air through buildings or other enclosed areas. The vast majority of HVAC systems heat, cool, or ventilate a building by converting energy into heat or mechanical energy to move air inside.
HVAC systems can be installed on the roof as well as on-site for maximum utility, or be utilized inside specific rooms.
They increase energy efficiency by keeping temperatures consistent in your house which means you can save quite a bit of money on your energy bills in the long run. HVAC systems can also reduce allergens in the air.







